The green revolution is essential, but despite massive investments in renewable energy, real-world progress is being held back by persistent bottlenecks and outdated systems.
1. Grid & Transmission Bottlenecks
- China’s wind power boom is being throttled: Wind farms in Gansu—among the largest in the world—frequently operate below 40% capacity due to insufficient transmission infrastructure (wired.com).
- UHV lines lag behind installations: While ultra-high-voltage projects aim to bridge the gap between renewable-rich regions and demand centers, grid development remains slower than generation build-out (caixinglobal.com).
- Grid designed for coal, not renewables: Much of China’s energy grid favors centralized fossil-fuel plants, making it ill-equipped for distributed, intermittent renewables.

2. Bureaucratic Hurdles & Red Tape
- Projects get built, but can’t plug in: A UK wind farm may take just months to construct, yet seven years to connect—a paradox flagged as a major issue by Octopus Energy’s CEO (wired.com).
- The US backlog is crippling. Over 2,600 GW of renewable projects await grid approval in the US—a clear disruption calling for streamlined, tech-led interconnection processes (theverge.com).
3. The ‘Green Bubble' & Overcapacity Risks
- China’s solar & wind output is tremendous but underutilized: Overcapacity in manufacturing has driven prices down, yet much energy remains untapped due to poor grid absorption.
- Economic vulnerability looms: Some warn that green-energy overbuilding could trigger a market bubble if investments outpace practical integration (wired.com).
4. Why AI and Smart Tech Matter
- AI is a game-changer for grid interconnection: The US DOE's AI4IX program is investing US$ 30 million to accelerate grid tying, aiming to slash years off the queue (theverge.com).
- Optimization via AI: Smarter forecasting and predictive maintenance promise to help renewables sync better with existing grids, boosting efficiency.
5. Persistent Coal Dependence
- China still builds coal plants: Even with massive clean energy rollouts, new coal capacity continues to be approved, in 2024 alone adding almost 67 GW (theguardian.com).
- Fossil fuel inertia: Coal's entrenched status, resistant grid infrastructure, and political lobbying ensure it remains difficult to fully displace.
➤ The Big Picture
The green revolution isn't faltering due to a lack of ideas or investment; it’s struggling against the practical limits of infrastructure, outdated regulations, economic mismatches, and political inertia. Without urgent reform in grid modernization, streamlined policies, and AI integration, we risk underutilizing clean energy, even as we build it.
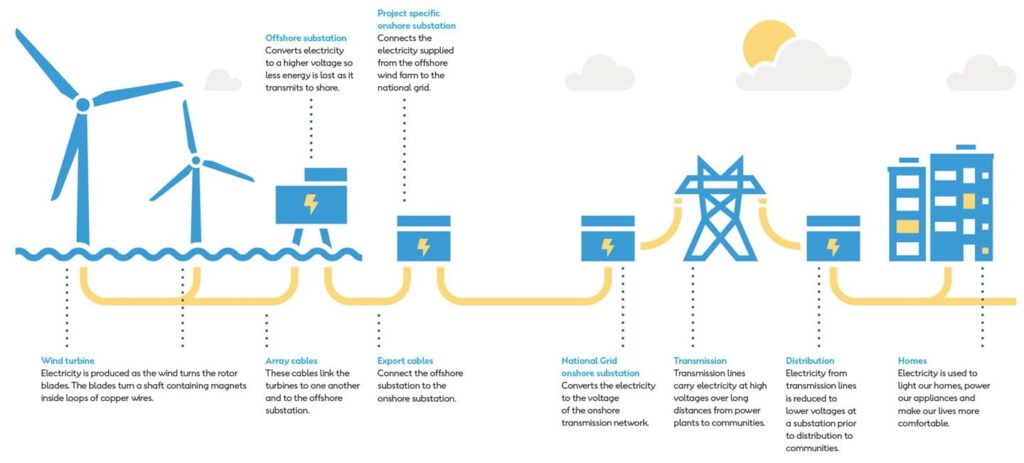
✅ Solutions on the Horizon
- Massive grid modernization: Countries must rapidly build ultra-high-voltage lines and microgrids designed for renewables (elearncollege.com).
- Bureaucratic overhaul: Regulators need radical simplification—akin to removing seven years of red tape per wind connection (wired.com).
- AI to the rescue: From interconnection approval to real-time energy balancing, smarter systems can bridge the integration gap (theverge.com).
🔚 Closing Thoughts
The green revolution isn’t just about generating sun and wind—it’s about weaving them into the fabric of our global energy systems. Only when policy, infrastructure, and technology evolve together will the clean-energy potential be fully realized.
Curious to explore more green-energy challenges and breakthroughs? Check out this in-depth article on renewable grid integration—and drop a comment on what solutions you’d like to see next!

Want to Explore More?
Read our latest piece: Green Technologies of the Future: Which Developments Will Save the World?.
Comment below: What’s your take on the environmental cost of green tech?
Tag us on social media using #GreenTechRealityCheck
Have questions or thoughts? Comment below and let us know what more you’d like to learn about green technology—we’d love to hear from you!









