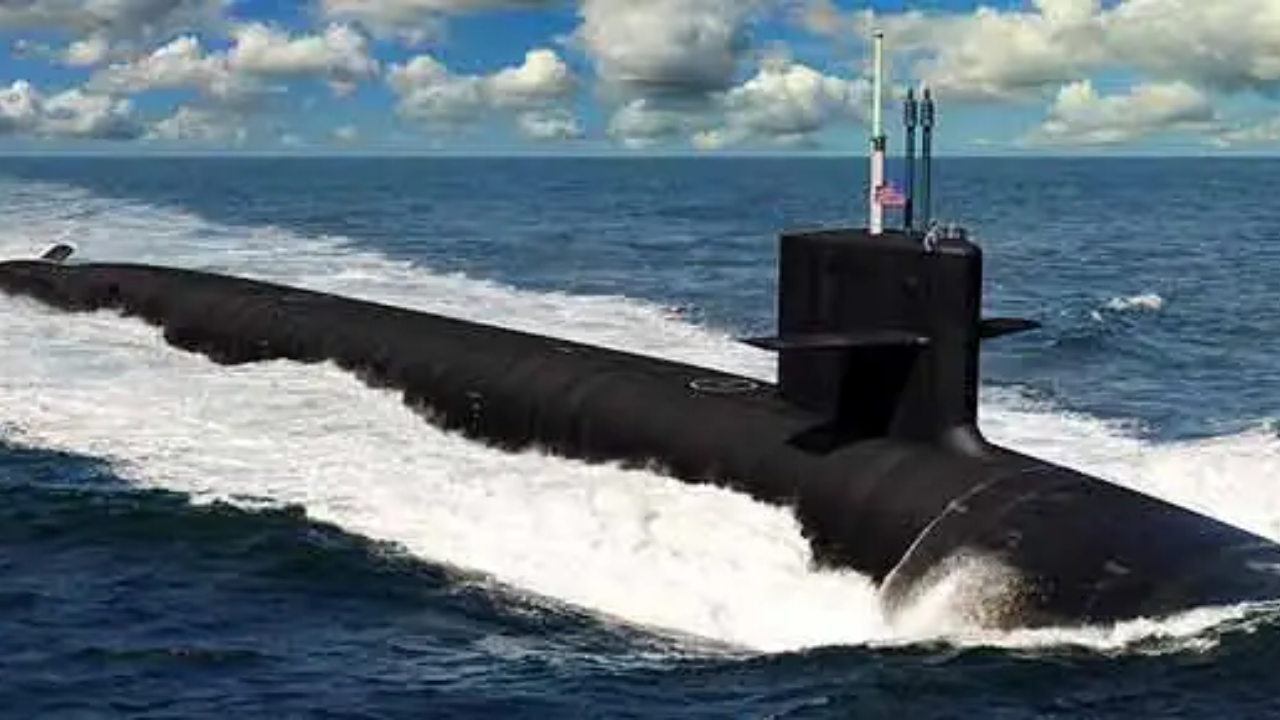
Submarines, long hailed as the silent hunters of the deep, are undergoing a revolutionary transformation driven by cutting-edge technology. From enhanced stealth to autonomous capabilities and advanced weaponry, the latest developments in submarine technology are reshaping naval warfare and undersea exploration. This continuous evolution is crucial for maintaining strategic advantage and addressing emerging global challenges, with significant investments and innovations coming from leading defense contractors and national navies, particularly in the US.
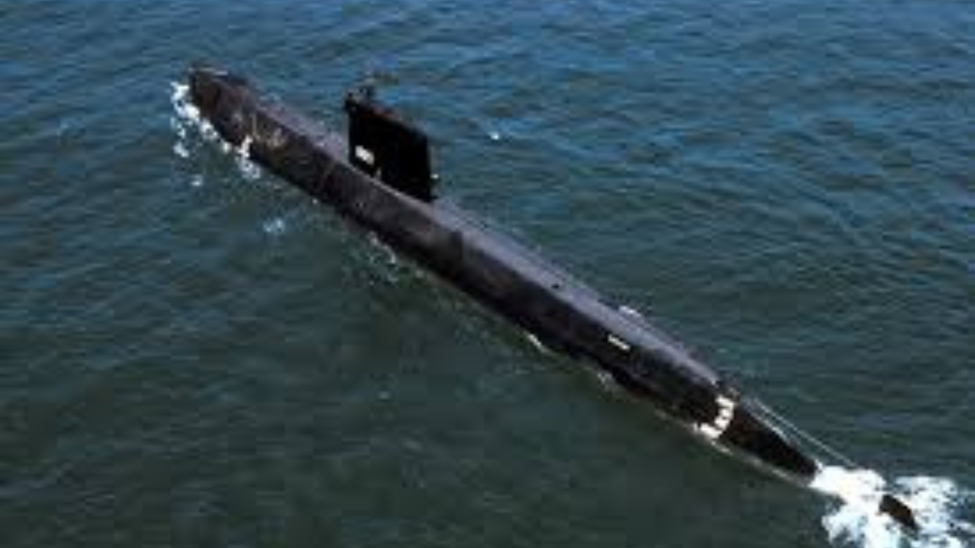

Latest Developments in Submarine Technology
The pace of innovation in submarines technology is accelerating, with a focus on several key areas:
1. Enhanced Stealth and Acoustic Superiority
The ability to remain undetected is paramount for submarines. Innovations in submarine technology are centered on further reducing acoustic signatures through advanced quieting techniques. This includes improved anechoic coatings that absorb sonar pulses, quieter propulsion systems like pump-jets and integrated electric propulsion, and advanced noise cancellation technologies. Hull design is also being refined for optimal hydrodynamic efficiency, minimizing turbulence and radiated noise. These advancements aim to make the latest generation of submarines virtually silent in the vastness of the ocean, significantly improving their survivability and operational effectiveness.
2. Advanced Sensor and Sonar Systems
Modern submarines are equipped with highly sophisticated sonar arrays – both passive (listening for sounds) and active (emitting sound waves) – capable of detecting targets at greater ranges and with higher fidelity. Developments in submarine technology include integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to process vast amounts of acoustic data, enabling faster and more accurate target classification and reducing false alarms. Quantum sensors are also under research, promising revolutionary capabilities for underwater detection and navigation.
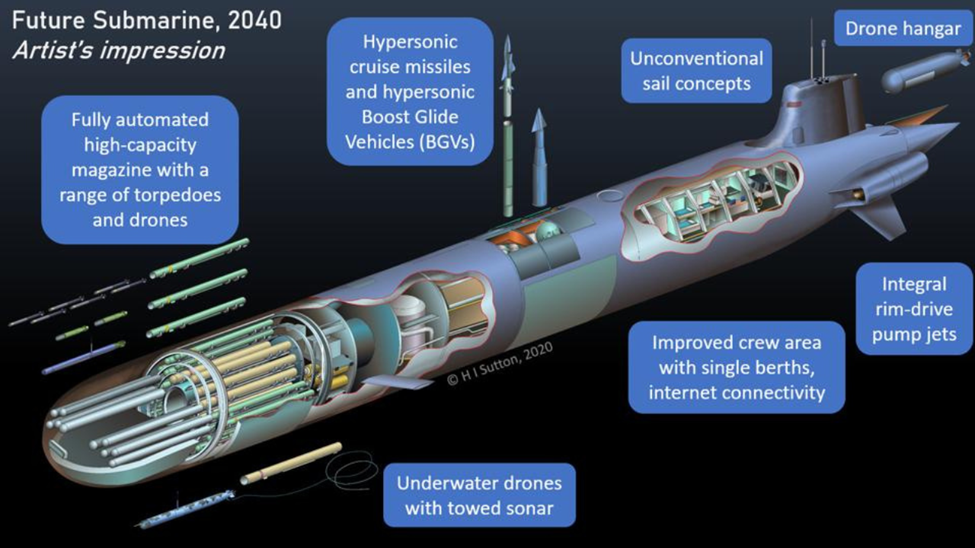
3. Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Unmanned Systems
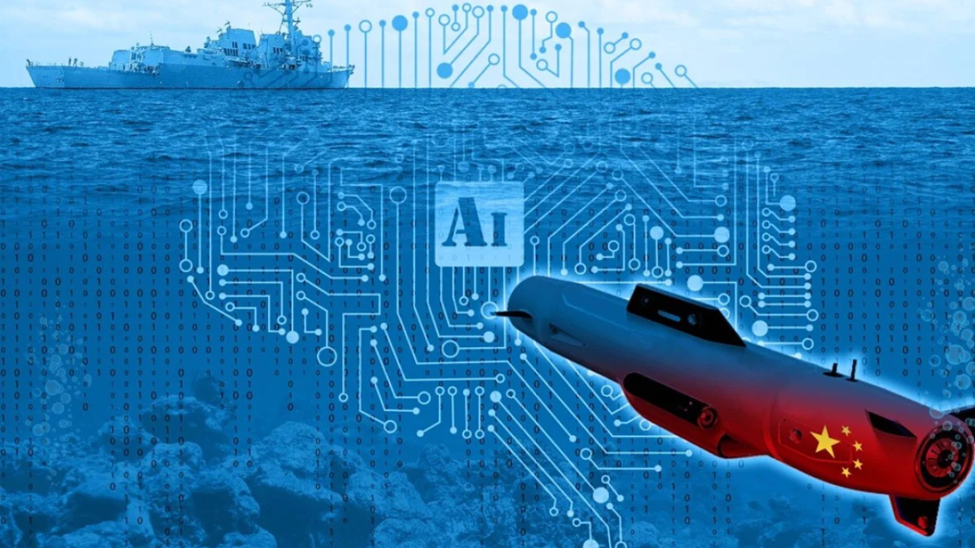
The integration of AUVs into submarine operations represents a significant leap in submarine technology. These unmanned platforms can extend a submarine's reach, conducting reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and even offensive operations while the manned submarine remains at a safe distance. Future concepts envision large, highly automated fleets of submarines acting as “mother ships” for swarms of smaller, AI-controlled AUVs, creating a distributed and highly lethal undersea network.
4. Next-Generation Propulsion Systems
While nuclear propulsion remains critical for long-endurance submarines, advancements in Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) for conventional submarines are making them quieter and capable of staying submerged for weeks without needing to surface for air. Research is also ongoing into entirely new forms of propulsion that could offer even greater speed, endurance, and stealth. These innovations are driving the evolution of submarine technology.
5. Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI is profoundly impacting submarine technology. Beyond sonar data processing, AI is being applied to optimize navigation, predict equipment failures for predictive maintenance, and manage complex combat systems. The goal is to reduce crew workload, enhance decision-making under pressure, and ultimately pave the way for a fully autonomous or highly automated submarine that can operate for extended periods with minimal human intervention. This is a critical area of innovation in submarine technology.
6. Weapon Systems and Integration
Submarines are becoming platforms for an increasingly diverse array of weaponry. This includes advanced torpedoes, long-range cruise missiles for land attack and anti-ship roles, and potentially even anti-air capabilities for self-defense. The integration of AI into torpedoes, as seen in recent reports on Chinese developments, makes them faster and smarter, able to better discriminate between targets and decoys. This continuous enhancement of offensive capabilities is a key element of submarine technology.
7. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
3D printing is revolutionizing manufacturing and maintenance within the submarine industry. It allows for the rapid production of complex parts onboard or closer to the point of need, reducing lead times for critical components and improving fleet availability. This is a significant innovation in submarine technology, allowing for greater efficiency and readiness.
Submarine Technology Companies and Purchase
The development and acquisition of submarine technology involve a complex ecosystem of defense contractors and government procurement processes.
Key Companies: Leading companies in submarine technology include:
- General Dynamics Electric Boat (US): A primary builder of the US Navy's nuclear-powered submarines, including the Virginia-class and Columbia-class ballistic missile submarine.
- Huntington Ingalls Industries (US): Also a major contributor to US submarine construction and fleet services.
- BAE Systems (UK): Responsible for the design, build, testing, and commissioning of the Royal Navy's submarines, such as the Astute-class.
- Naval Group (France): A global leader in naval defense, designing and building a wide range of submarines.
- ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (Germany): Known for its conventional (diesel-electric) submarines.
- Saab AB (Sweden): Also produces highly advanced conventional submarines.
- HD Hyundai Heavy Industries (South Korea): A growing influence in Asia-Pacific, developing competitive conventional submarines.
- Lockheed Martin Submarines: While not a primary builder of entire submarines, Lockheed Martin is a crucial supplier of advanced systems and technologies for them. They are a major provider of submarine combat systems for the US Navy and other countries, serving as the combat system integrator for various submarine classes. Their contributions include sonar systems, navigation, electronic warfare systems (such as the AN/BLQ-10(V) that rapidly analyzes critical signals), and missile launch systems. Their involvement highlights the modular nature of modern submarine technology acquisition, where specialized companies contribute vital components.

Submarine Technology Purchase
The procurement of submarine technology is typically a government-to-government or government-to-contractor process, often involving multi-billion dollar contracts over many years. Nations may purchase complete submarine platforms, license technology for indigenous production, or acquire specific subsystems and components. There's also a growing interest in “submarines-as-a-service” models, where navies might lease conventionally powered submarines from commercial entities for training and RDT&E (research, development, test, and evaluation), thereby freeing up their high-end nuclear attack submarine for critical missions. This model can accelerate the integration of new submarine technology.
US Submarine Technology
The US submarine technology program is among the most advanced globally, with a strong emphasis on maintaining undersea dominance. Key elements include:
1. Virginia-class Attack Submarine (SSN)
These highly capable nuclear-powered attack submarines incorporate advanced stealth, sophisticated sensors, and the ability to launch various weapons, including cruise missiles and torpedoes. Ongoing upgrades continuously integrate the latest submarine technology.
2. Columbia-class Ballistic Missile Submarine (SSBN)
Designed to replace the aging Ohio-class, the Columbia-class represents the pinnacle of strategic deterrence. These submarines will incorporate new stealth technologies and nuclear propulsion systems designed for extended patrols, ensuring the survivability of the nation's nuclear deterrent. This class represents a significant investment in submarine technology.
3. Future Attack Submarine (SSN(X))
The US Navy is also planning for its next-generation attack submarine, which is expected to integrate even more disruptive submarine technology, including advanced automation, next-generation sensors, and potentially directed energy weapons.

4. Undersea Networked Warfare
A key focus for US submarine technology is connecting submarine with other naval assets, including unmanned systems and surface vessels, through robust and secure communication networks to achieve greater situational awareness and coordinated action in the undersea domain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the innovations in submarine technology are transforming these vessels into increasingly stealthy, intelligent, and lethal platforms. The relentless pursuit of advancements in acoustics, AI, automation, propulsion, and materials is not only pushing the boundaries of engineering but also fundamentally altering naval strategies. As global competition intensifies, the continued development and acquisition of cutting-edge submarine technology will remain a critical priority for leading naval powers around the world.









