The global food system faces unprecedented challenges: a rapidly growing population, diminishing arable land, unpredictable climate patterns, and increasing demand for fresh, locally sourced produce. Traditional farming methods, while foundational, are often resource-intensive and vulnerable to environmental fluctuations. In response to these pressures, vertical farming has emerged as a revolutionary approach, poised to redefine the future of agriculture. By growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often indoors and in controlled environments, vertical farming promises higher yields, reduced resource consumption, and year-round production, representing a significant leap in farming technology.

What is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming is an innovative agricultural method where crops are grown in vertically stacked layers, often indoors and in controlled environments. This approach utilizes specialized technologies such as LED lighting systems, precise climate control, and soilless growing techniques like hydroponics (Growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil), aeroponics (Misting plant roots with nutrient solutions in an air or mist environment), or aquaponics (A system that combines aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) with hydroponics, where the waste from fish provides nutrients for the plants) to optimize plant growth.
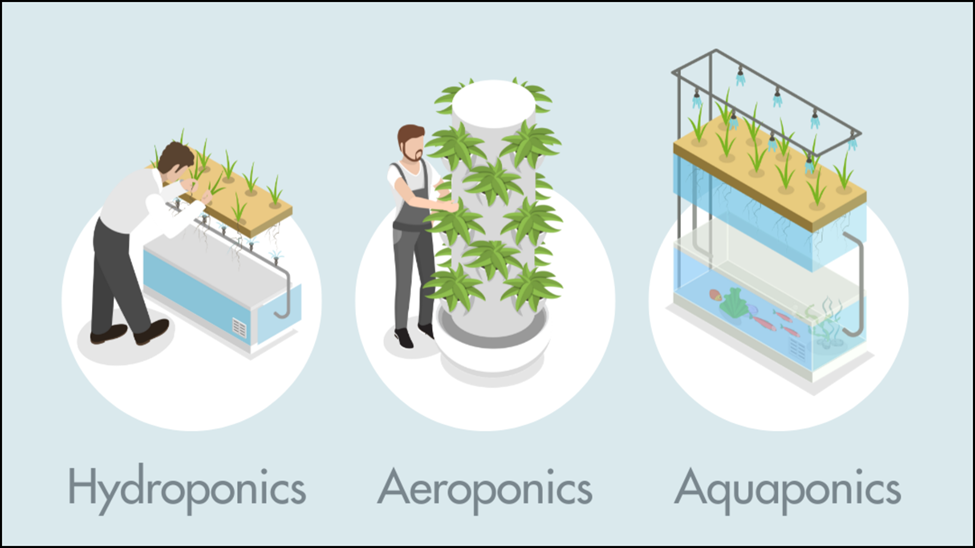
It aims to produce higher yields, reduce resource consumption (especially water and land), and enable year-round production, making it a sustainable solution for food security, particularly in urban areas.
Is Vertical Farming the Future of Agriculture?
The concept of vertical farming as the future of agriculture stems from its ability to overcome many limitations of conventional farming. It brings food production closer to urban centers, reducing transportation costs and carbon footprints. Imagine fresh produce grown just miles from your grocery store, available regardless of season or local climate. This paradigm shift makes farming a compelling solution for food security in a world grappling with urbanization and climate change.

At its core, vertical farming leverages technology to create optimal growing conditions. This includes sophisticated LED lighting systems tailored to specific plant needs, climate control systems to regulate temperature and humidity, and advanced hydroponic, aeroponic, or aquaponic methods that deliver nutrients directly to plant roots without soil. The result is a highly efficient and productive system that redefines our understanding of where and how food can be grown. This advanced farming technology is key to achieving consistent, high-quality yields.
5 Latest Innovations in Vertical Farming Technology
The sector of vertical farming is a hotbed of innovation, with continuous advancements refining its efficiency, scalability, and economic viability. Staying updated with these farming innovations blog posts and industry news is crucial for understanding the rapid progress in this field.
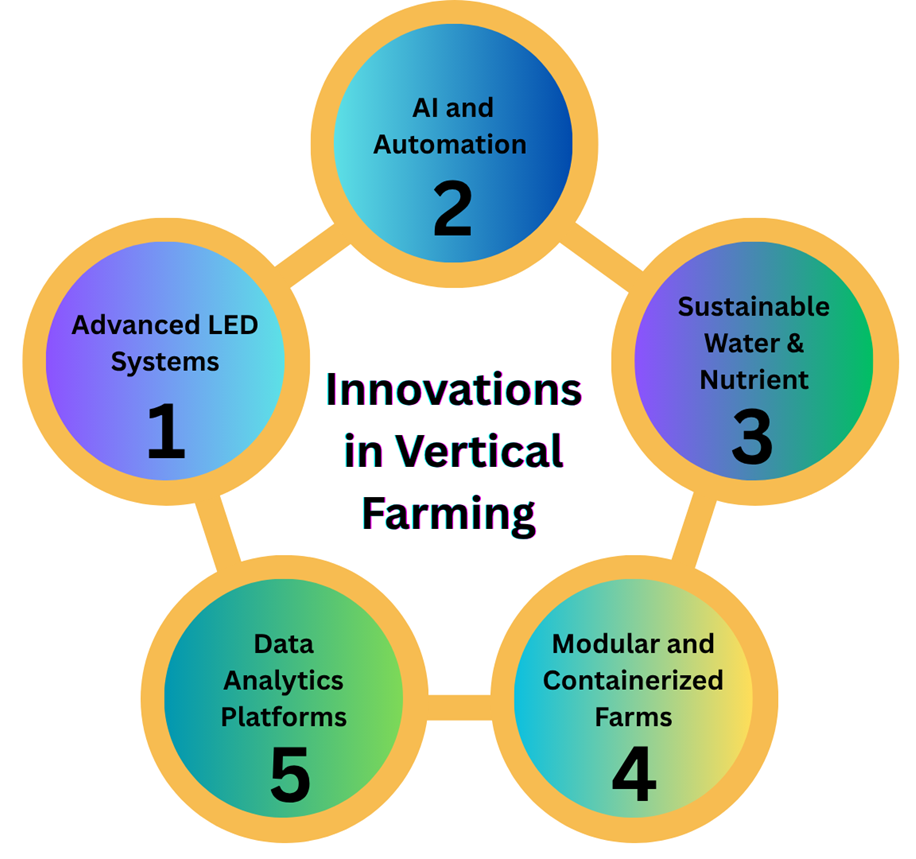
- Advanced LED Lighting Systems
- AI and Automation
- Sustainable Water and Nutrient Management
- Modular and Containerized Farms
- Data Analytics Platforms
1. Advanced LED Lighting Systems
Beyond basic LEDs, innovations now include dynamic spectral control, allowing growers to precisely adjust light wavelengths and intensity throughout a plant's growth cycle. This optimizes photosynthesis, enhances flavor profiles, and can even influence nutrient content. Pulsed lighting and UV treatments are also being explored for disease resistance and pest control.
2. AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence is central to optimizing farming operations. AI-powered sensors monitor everything from nutrient levels and CO2 concentrations to plant health and growth rates. Machine learning algorithms analyze this vast data to predict optimal growing recipes, identify potential issues early, and even automate tasks like planting, harvesting, and pest detection. Robotic systems are increasingly integrated for precision tasks, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency.
3. Sustainable Water and Nutrient Management
Hydroponics (growing in nutrient-rich water), aeroponics (misting roots with nutrients), and aquaponics (combining aquaculture with hydroponics) are fundamental to vertical farming. Recent innovations focus on hyper-efficient closed-loop systems that recycle nearly 100% of the water, significantly reducing water consumption compared to traditional field farming. Nutrient delivery systems are becoming more precise, minimizing waste and optimizing plant uptake.
4. Modular and Containerized Farms
The development of modular and containerized farming systems has made this technology more accessible and scalable. These self-contained units, often built within repurposed shipping containers, can be deployed rapidly in diverse locations, from urban rooftops to remote communities, offering local food production anywhere. Businesses looking to enter the market might even consider where they can buy vertical farming systems that are pre-fabricated.
5. Data Analytics Platforms
Sophisticated software platforms now integrate data from all aspects of the vertical farm, providing growers with real-time insights and predictive analytics. This allows for data-driven decision-making, continuous optimization of growing conditions, and identification of best practices. These platforms are often discussed on vertical farming innovations blog posts.
Benefits of Vertical Farming
The advantages of vertical farming are compelling and address many critical challenges in modern agriculture:
1. Year-Round Production
Unaffected by external climate conditions, vertical farms can produce crops 365 days a year, ensuring consistent supply and stable pricing.
2. Reduced Land Use
By growing vertically, these farms can produce significantly more food per square foot of land compared to traditional farming, making them ideal for urban areas where space is limited.
3. Dramatic Water Savings
Hydroponic and aeroponic systems use up to 95% less water than field farming, as water is recycled in a closed loop, a crucial benefit in water-scarce regions.
4. No Pesticides/Herbicides
Controlled indoor environments largely eliminate pests and diseases, removing the need for harmful chemical pesticides and herbicides, resulting in cleaner, safer produce.
5. Reduced Transportation Costs & Emissions
Locating vertical farms near consumption centers drastically cuts down on “food miles,” lowering transportation costs and carbon emissions.
6. Predictable Yields & Quality
Controlled environments lead to consistent quality, size, and nutritional content, making planning and supply chain management more reliable.
2 Key Players and Global Adoption
1. US Vertical Farming
Companies like Aerofarms vertical farming are at the forefront of demonstrating the commercial viability and scalability of this technology. AeroFarms, based in the US, is known for its proprietary aeroponic systems and commitment to data-driven farming. They have developed advanced LED recipes and nutrient solutions, yielding produce with superior taste and texture. Their consistent appearance on vertical farming innovations blog platforms highlights their pioneering role.
2. India Vertical Farming
Meanwhile, India vertical farming is gaining traction as a sustainable solution to address food security for its vast population, particularly in urban areas with limited agricultural land. Challenges like water scarcity and climate variability in India make vertical farming an increasingly attractive option, with pilot projects and commercial ventures emerging across the country. Governments and private entities in various nations are exploring how to integrate vertical farming into their national food strategies, showcasing its global relevance as a burgeoning farming technology.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the immense promise, vertical farming still faces hurdles. High initial setup costs, significant energy consumption for lighting and climate control (though this is being mitigated by LED and renewable energy advancements), and the limited range of economically viable crops (primarily leafy greens and herbs) are current constraints. However, ongoing research and innovations are continually addressing these issues. Future farming technology will likely see increased automation, lower energy demands through more efficient lighting and renewable energy integration, and the expansion to a wider variety of crops, including fruits and vegetables.
The continuous stream of vertical farming innovations blog posts, the growth of companies like Aerofarms vertical farming, and the global adoption seen in regions like India vertical farming all point to a future where vertical farming plays an indispensable role in sustainable food production. It's not just a niche agricultural practice; it's a vital component of a resilient, resource-efficient, and urban-integrated food system. The question is no longer if vertical farming will be part of the future of agriculture, but how rapidly its technology will evolve to feed a growing world.








