The question of how life first arose from non-living matter, a process known as abiogenesis, remains one of science's most profound and challenging mysteries. Far from being a settled debate, the field of abiogenesis research is incredibly active, with new discoveries constantly refining our understanding of the conditions and chemical reactions that could have led to the emergence of life on early Earth. This quest to understand abiogenesis bridges chemistry, biology, geology, and even astronomy, offering tantalizing clues about life's potential beyond our planet.
What is Abiogenesis?
It is the scientific theory that life originated from non-living organic compounds through natural processes, gradually transitioning from simple molecules to complex, self-replicating systems. This is distinct from the discredited concept of “spontaneous generation,” which posited that complex organisms (like maggots or mice) could arise continually from decaying matter.
Instead, it proposes a gradual, stepwise chemical evolution that occurred billions of years ago when Earth's conditions were vastly different from today. It seeks to explain how the fundamental building blocks of life – amino acids, nucleotides, lipids, and carbohydrates – formed and then assembled into the first protocells, capable of metabolism and replication. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities was not a single event, but a process of increasing complexity.
Latest Research on Abiogenesis: Breakthroughs and Shifting Paradigms
Recent breakthroughs in abiogenesis research are pushing the boundaries of what was once thought possible in a laboratory setting, offering new insights into key stages of life's origin:
1. “Microlightning” and Droplet Chemistry
One fascinating recent development challenges the traditional view of atmospheric lightning as the sole electrical spark for prebiotic chemistry. Research published in Science Advances (March 2025) suggests that “microlightning” – weak electrical charges generated in water microdroplets created by crashing waves and splashing water – could have provided the energy needed for the formation of organic molecules. Experiments demonstrated that spraying water microdroplets into gas mixtures containing nitrogen, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia produced key organic molecules like hydrogen cyanide, uracil, and glycine. This highlights the importance of air-water interfaces as potential “peptide
factories” in the early Earth, potentially solving the “water paradox” where the formation of peptides (which involves water loss) would be thermodynamically unfavorable in a watery environment. This is a significant step in understanding the early stages of abiogenesis.
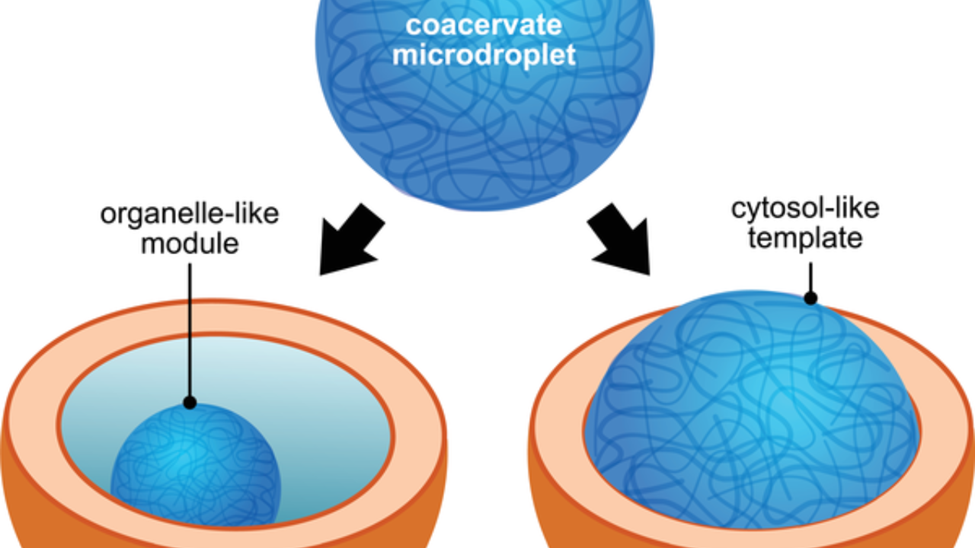
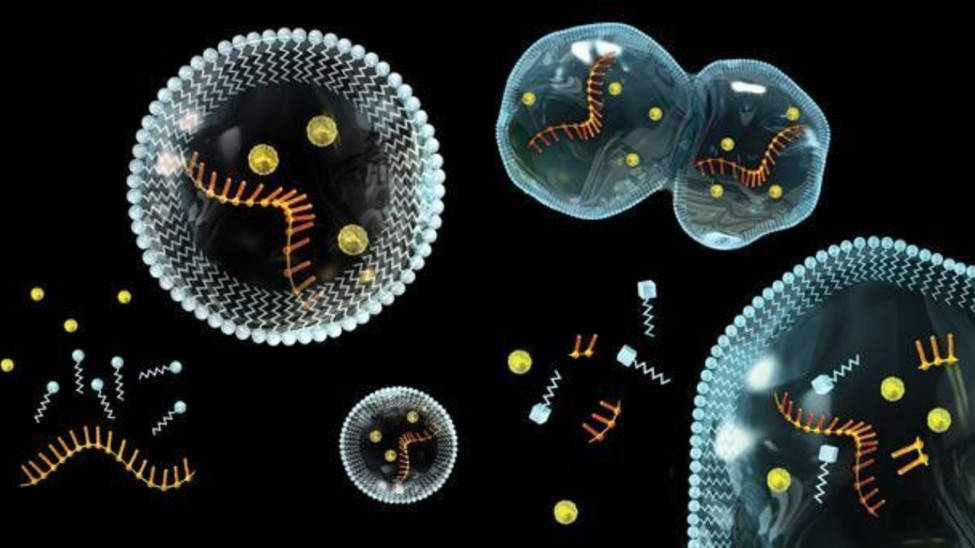
2. Self-Replicating Droplets (Coacervates)
A breakthrough by Japanese scientists, published in Nature Communications (April 2025), demonstrated the first laboratory-controlled self-reproducing coacervate droplets. Coacervate droplets are tiny clusters of molecules that can encapsulate biomolecules and mimic cell-like behaviors. This research, using amino acid thioesters, demonstrated that these synthetic droplets could not only form but also reproduce, suggesting a “droplet world” hypothesis in which such structures could have evolved into complex molecular aggregates capable of replication, organization, and survival. This challenges the long-standing “RNA world” hypothesis by proposing an earlier stage of cellular organization in the process of abiogenesis.
3. Revisiting the Formose Reaction
A new study published in Chem (May 2025) by Scripps Research and Georgia Institute of Technology scientists is prompting a serious reconsideration of the “formose reaction,” a 160-year-old theory that proposed ribose (a sugar vital for RNA) arose spontaneously from formaldehyde under prebiotic conditions. Their findings indicate that under realistic early Earth conditions (room temperature, pH 8), the formose reaction does not produce the linear sugars necessary for RNA, but rather branched structures. This doesn't disprove abiogenesis, but suggests that other pathways for the prebiotic synthesis of essential sugars need to be explored, highlighting the ongoing refinement of our understanding of chemical abiogenesis.
4. The RNA World Hypothesis Refinements
The “RNA world” hypothesis, which posits that early life utilized RNA for both genetic information storage and catalytic functions before DNA and proteins emerged, remains a central pillar of abiogenesis. Recent work continues to explore how RNA molecules could have self-replicated and evolved in the absence of complex enzymes, focusing on the spontaneous formation of RNA components and the catalytic capabilities of ribozymes. Research aims to elucidate how this RNA-based system could have transitioned to the DNA-protein world we see today, a crucial step in the overall understanding of abiogenesis.
Finding Abiogenesis Studies: PubMed Research and Beyond
Researchers actively publish their findings on abiogenesis in a wide array of scientific journals. To find the latest studies, including those relevant to US biology research, one can utilize:

- PubMed: A primary database for biomedical literature, PubMed is an excellent resource. Searching terms like “abiogenesis,” “origin of life,” “prebiotic chemistry,” “RNA world,” and “protocell” will yield numerous relevant articles, often with links to full text or abstracts.
- Google Scholar: A broader search engine for academic literature, Google Scholar can cast a wider net, including papers from chemistry, geology, and astrophysics journals relevant to abiogenesis.
- Scientific Journals: Directly following journals such as Nature, Science, PNAS, Astrobiology, Origins of Life and Evolution of Biospheres, Chemical Communications, and Journal of the American Chemical Society will provide updates on new abiogenesis research.
- Research Institutions: Many universities and research institutions, particularly in the US, have active groups working on abiogenesis and related fields of evolutionary biology. Their websites often feature recent publications and news.
Evolutionary Biology and the Impact of Abiogenesis Research
Abiogenesis is distinct from, yet intimately linked with, evolutionary biology. Evolutionary biology studies how life diversified and changed after it first arose, while it focuses on that initial spark of life. However, discoveries in abiogenesis profoundly impact evolutionary biology by providing a
scientific basis for life's starting point. Understanding how the first self-replicating entities emerged allows evolutionary biologists to build more complete models of early life and the Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA) of all extant life. Research into LUCA, for instance, informs abiogenesis by suggesting characteristics of the earliest cells. The insights from abiogenesis research also extend to astrobiology, informing the search for extraterrestrial life by identifying plausible conditions and chemical precursors that could lead to life elsewhere in the universe. The interdisciplinary nature of abiogenesis continues to push the boundaries of our understanding of life itself. The field of abiogenesis is vibrant, constantly refining our theories. Each new study brings us closer to unraveling the profound mystery of abiogenesis.