The landscape of molecular biology has been profoundly reshaped by the discovery and subsequent elucidation of RNA Interference (RNAi). This intricate cellular mechanism, once a scientific curiosity, has blossomed into a powerful tool for research and a promising avenue for therapeutic development. Understanding its evolution, mechanisms, and applications provides a fascinating glimpse into the sophistication of biological regulation.
What is RNA Interference?
At its most fundamental level, RNA Interference is a biological process in which RNA molecules play a critical role in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression. This suppression can occur at various stages, primarily by preventing messenger RNA (mRNA) from being translated into proteins or by inhibiting transcription itself. Essentially, RNA Interference acts as a cellular “gene silencer,” finely tuning which genes are active and to what extent.

The key players in RNA Interference are small RNA molecules, primarily small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). These tiny, non-coding RNAs are typically around 20-25 nucleotides long. They guide a multiprotein complex called the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to target specific mRNA sequences. When RISC binds to its complementary mRNA target, it can either cleave and degrade the mRNA, preventing protein synthesis, or simply block translation, effectively silencing the gene. This remarkable mechanism highlights the sophisticated layers of regulation within a cell, demonstrating that genetic information flow isn't a one-way street from DNA to protein.
Evolution of RNA Interference: An Ancient Guardian
The evolution of RNA Interference is a story deeply intertwined with the fundamental survival strategies of living organisms. Initially observed in plants and fungi in the early 1990s as “post-transcriptional gene silencing” or “quelling,” its true significance was unveiled with the landmark discovery in Caenorhabditis elegans (a tiny worm). This work, demonstrating the potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA, provided the crucial breakthrough in understanding RNA Interference.
It is now widely accepted that RNA Interference evolved primarily as a cellular defense mechanism. Its ancient origins trace back to its role in protecting genomes against invading viruses and transposable elements (often called “jumping genes”). Double-stranded RNA, frequently produced by viral replication or transposable element activity, acts as a trigger for the RNA Interference pathway, leading to the degradation of these potentially harmful nucleic acids. Over evolutionary time, this protective system was co-opted and refined to regulate endogenous gene expression, becoming an indispensable part of normal cellular development and physiological processes in diverse eukaryotes, from plants and fungi to animals, including humans. This dual function underscores the evolutionary adaptability of RNA Interference.
How RNA Interference Works: A Molecular Dance
The mechanism of RNA Interference is a beautifully orchestrated molecular dance involving several key proteins. It typically begins with the presence of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), which can be exogenous (e.g., from a virus) or endogenous (e.g., from regulatory elements or aberrant transcripts).
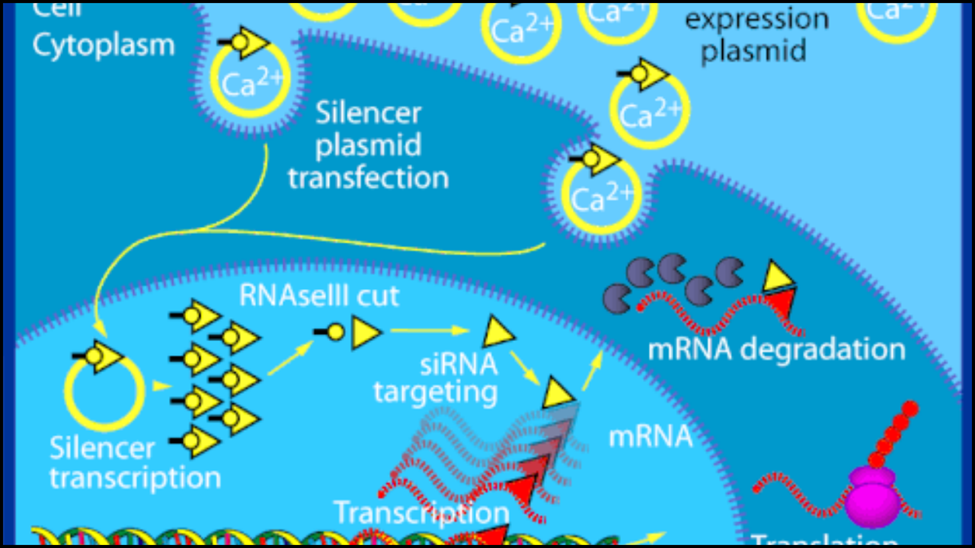
1. Dicing
An enzyme called Dicer, an RNase III enzyme, recognizes and cleaves these long dsRNAs into shorter fragments, approximately 21-25 nucleotides in length. These are known as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or, if derived from endogenous hairpin structures, microRNAs (miRNAs).
2. RISC Loading
The newly generated siRNAs or miRNAs are then loaded into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). During this loading, one strand of the double-stranded RNA is typically discarded, leaving a single-stranded guide RNA within RISC.
3. Target Recognition
The guide RNA within RISC acts like a molecular homing beacon, directing the RISC complex to complementary mRNA sequences in the cytoplasm.
4. Gene Silencing
Once RISC binds to its target mRNA, the outcome depends on the degree of complementarity.
If there is perfect or near-perfect complementarity (often the case with siRNAs), Argonaute (Ago), a key enzyme within RISC, cleaves and degrades the target mRNA. This prevents its translation into protein.
If there is imperfect complementarity (more common with miRNAs), RISC may instead inhibit translation of the mRNA, or lead to its decay, but without direct cleavage.
This precise and efficient mechanism makes RNA Interference a powerful regulator of gene expression.
Find RNA Research Papers: Navigating the Scientific Landscape
To find a wide range of RNA research papers, several online databases and resources are invaluable:
1. PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
This is the go-to resource for biomedical literature. Use keywords like “RNA interference,” “siRNA,” “miRNA,” “gene silencing,” and specific disease terms to narrow your search for relevant RNA research papers.
2. Google Scholar
A broad search engine for scholarly literature across various disciplines. It often links directly to full-text articles or institutional repositories.
3. Web of Science / Scopus
These subscription-based databases offer comprehensive citation indexing, allowing you to track the impact of RNA research papers and find related research.

4. Specific Journal Websites
Journals specializing in molecular biology, genetics, and cell biology (e.g., RNA, Cell, Nature, Science, Molecular Cell, Genes & Development) are excellent sources for RNA research.
5. Preprint Servers (e.g., bioRxiv, medRxiv)
These platforms host research papers before peer review, offering a glimpse into the latest, breaking RNA discoveries.
6. Professional Societies
Organizations like The RNA Society often have dedicated sections for publications and resources related to RNA Interference.
Nobel Prize RNA Research: Recognizing Groundbreaking Discoveries
The profound impact of RNA Interference on biology and medicine has been recognized with multiple Nobel Prizes, underscoring its significance.
1. 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Awarded to Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello “for their discovery of RNA interference – gene silencing by double-stranded RNA.” Their groundbreaking work in C. elegans solidified the understanding of RNA Interference as a fundamental biological process.

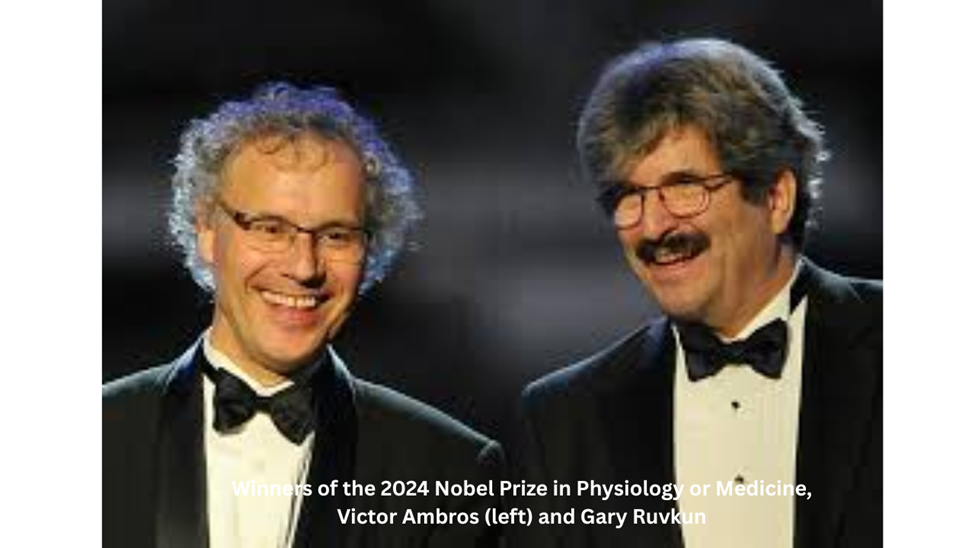
2. 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun “for the discovery of microRNA and its role in post-transcriptional gene regulation.” Their independent discoveries of tiny, non-coding RNAs that regulate vast networks of gene expression, building on the foundation of RNA Interference, further expanded our comprehension of cellular control.

It's also worth noting that other Nobel Prizes have touched upon RNA research, such as the 1989 Chemistry Prize for the discovery of RNA's catalytic properties (ribozymes) by Sidney Altman and Thomas Cech, and the 2023 Physiology or Medicine Prize for mRNA vaccine development. The ongoing recognition highlights the central and evolving role of RNA in biological understanding.
US Gene Science: Advancing RNA Interference Applications
The United States has been at the forefront of gene science, with significant investment and research driving advancements in RNA research. Government agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Science Foundation (NSF) provide substantial funding for basic and translational research in molecular biology, including extensive programs focused on gene regulation and RNA Interference.
This robust ecosystem of academic institutions, government funding, and a thriving biotechnology sector has propelled the development of RNA Interference from a laboratory phenomenon to a therapeutic strategy. US-based companies are actively developing RNA Interference-based drugs for various diseases, including rare genetic disorders, viral infections, and cancers. Initiatives to streamline gene therapy development and accelerate clinical trials for RNA therapeutics are also a major focus. The US regulatory environment, while stringent, also provides a clear pathway for the approval of novel gene-based medicines, including those leveraging RNA research.
Molecular Biology: The Home of RNA Interference
RNA Interference is fundamentally a cornerstone of molecular biology. Its discovery and ongoing study have illuminated crucial aspects of gene expression, regulation, and cellular defense mechanisms. Molecular biology provides the framework for understanding the intricate interactions between RNA, DNA, and proteins that underpin RNA Interference.
Researchers in molecular biology continue to unravel new nuances of RNA Interference pathways, identify novel small RNAs, and explore their roles in health and disease. This field provides the tools and techniques necessary to:
- Manipulate Gene Expression: RNA Interference allows scientists to specifically “knock down” the expression of individual genes, providing invaluable insights into gene function.
- Understand Disease Mechanisms: Dysregulation of RNA Interference pathways is implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and viral infections. Molecular biologists study these alterations to identify potential therapeutic targets.
- Develop Therapeutics: The ability of RNA Interference to specifically silence disease-causing genes makes it an attractive therapeutic modality. Molecular biology is crucial for designing, delivering, and optimizing RNA Interference-based drugs.
The exploration of RNA Interference continues to be a vibrant and rapidly evolving area within molecular biology, promising further breakthroughs in our understanding of life and our ability to combat disease.








