Why Transparency Matters in Agriculture
Today’s consumers want to know more than just what’s on their plate—they want to know where it came from, how it was grown, and who produced it. But achieving this level of transparency in the global food system is easier said than done.
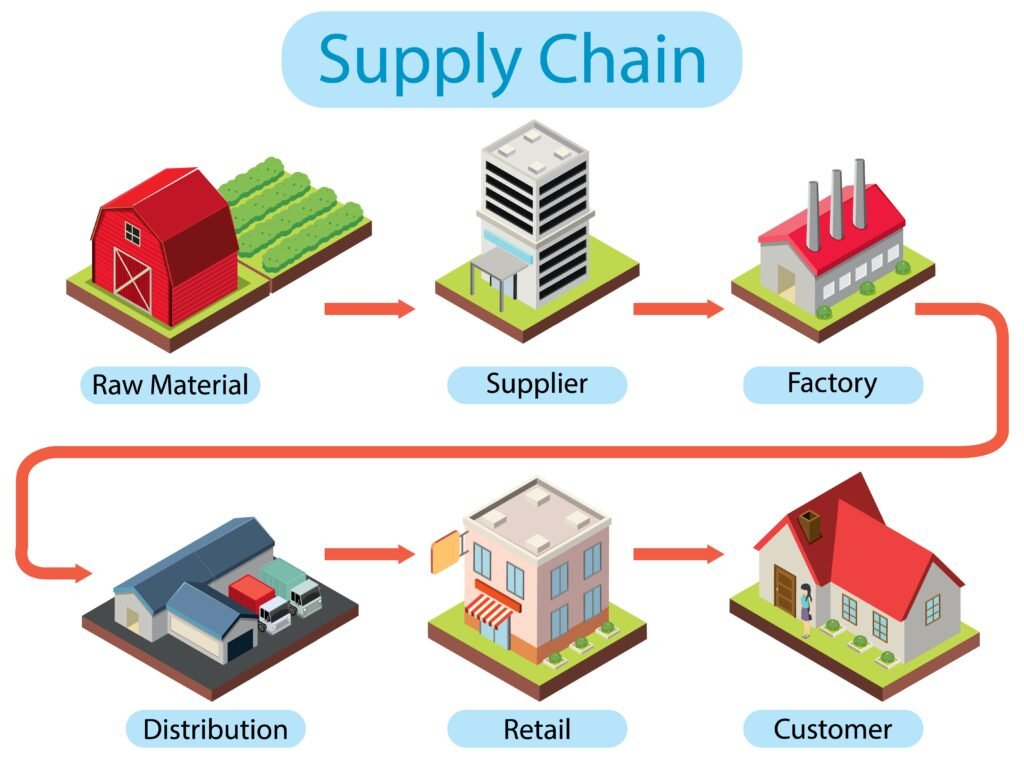
Traditional agricultural supply chains are complex, involving multiple intermediaries—from farmers and processors to transporters, exporters, wholesalers, and retailers. Unfortunately, this complexity leaves room for inefficiencies, fraud, contamination, and waste.
Enter blockchain in agriculture—a groundbreaking solution that’s bringing traceability, accountability, and real-time data sharing into the heart of farming and food logistics. In this blog, we’ll explore how blockchain is used in agricultural supply chains, its key benefits, real-world applications, and how it's transforming farm-to-fork transparency.
What is Blockchain, and Why Agriculture Needs it?
At its core, blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a secure, immutable, and transparent way. Each entry (or “block”) is linked to the previous one, making the data tamper-proof and verifiable by all participants in the chain.
In the context of agricultural supply chains, this means every step—from planting to packaging to retail—can be recorded, timestamped, and verified on a single, shared platform.
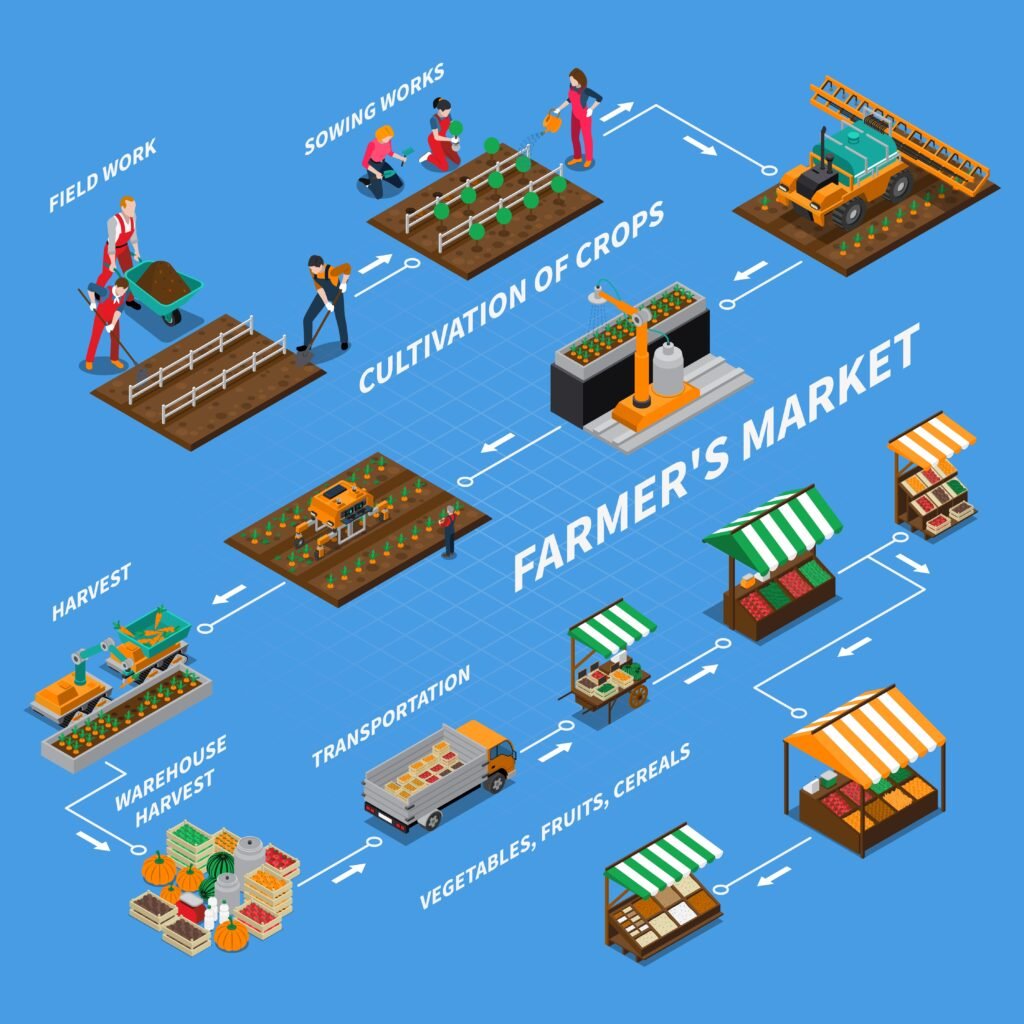

How Blockchain Works in Farming
Let’s break it down with a simple example:
- A farmer plants organic tomatoes.
- A blockchain record is created with seed information, date of sowing, and location.
- As the tomatoes grow, data about fertilizer use, watering schedules, and pesticide application is logged.
- When the tomatoes are harvested, they’re scanned and tagged with a QR code.
- The transportation company updates delivery records to the processor.
- The processor logs quality testing data and packaging info.
- At the retail store, the consumer scans the code to see the full farm-to-fork journey.
This kind of blockchain-based solution for farm-to-fork tracking ensures no part of the chain is hidden or falsified.
Key Benefits of Blockchain in Agriculture
Using blockchain technology in farming delivers a wide range of advantages for farmers, consumers, businesses, and regulators alike:
1. End-to-End Traceability
With blockchain, every product’s history is available in real time. This boosts food supply chain transparency and helps build consumer trust.
2. Reduced Food Fraud
Counterfeit organic labels or misrepresented origin claims are major problems. Blockchain for traceability ensures data integrity and combats food fraud in agriculture.
3. Faster Recall and Response
In the event of a contamination or safety concern, authorities can quickly identify the source and remove only affected batches—saving time, money, and lives.
4. Better Market Access for Farmers
Smallholders often struggle to prove the quality of their produce. Blockchain enables them to provide digital proof of compliance, making it easier to enter agricultural export markets.
5. Enhanced Sustainability
By recording every input and process, blockchain encourages eco-friendly choices. It promotes blockchain for sustainable agriculture practices, helping producers align with environmental standards.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Agricultural Supply Chains
Across the globe, companies and governments are embracing blockchain to enhance transparency in farming:
1. IBM Food Trust & Walmart
Walmart partnered with IBM to implement blockchain for tracking mangoes and pork. The result? What once took 7 days to trace now takes just 2.2 seconds.
2. TE-Food (Vietnam & Germany)
This platform enables real-time tracking of crops using blockchain, with data from farm, transport, slaughterhouse, and retail all available via mobile apps.
3. AgriDigital (Australia)
A blockchain platform for grain supply chains, offering payment security and provenance tracking to farmers, buyers, and banks.
4. GrainChain (Latin America & US)
Designed for small and mid-sized farmers, GrainChain allows blockchain-based transactions between growers, storage units, and exporters.
Global Impact: Blockchain in Developing Countries
Blockchain applications for agricultural exporters are especially useful in regions where corruption, poor record-keeping, and informal trade are barriers to global markets.
In East Africa, blockchain is helping coffee cooperatives certify their beans as organic and fair trade. In India, rice exporters are using blockchain to assure buyers of authenticity and pesticide-free production. In Latin America, cocoa farmers are gaining access to premium chocolate brands through verified blockchain-backed sourcing.
These innovations are enhancing transparency in agriculture through blockchain, while empowering small farmers economically.

Challenges to Adoption
While the potential is massive, adopting blockchain in agricultural supply chains comes with a few hurdles:
- Digital Literacy: Many farmers are still unfamiliar with mobile apps or blockchain platforms.
- Cost & Infrastructure: Initial setup for IoT sensors and QR code tags can be expensive.
- Data Accuracy: Blockchain can only guarantee what is entered—so if someone inputs false data, the system can’t correct it.
- Connectivity Issues: Rural areas may lack internet access or mobile coverage necessary for real-time updates.
These issues are being addressed through training programs, public–private partnerships, and low-tech blockchain integrations via SMS and mobile wallets.
The Future of Blockchain in Agriculture
Here’s what the future holds for blockchain in agriculture:
1. IoT & AI Integration
When combined with drones, sensors, and AI tools, blockchain will provide even smarter supply chain tracking and climate-resilient farming analytics.
2. Smart Contracts
Automated payments can be triggered when certain conditions are met (e.g., when crops arrive at port), reducing disputes and delays.
3. Farmer-Owned Platforms
Cooperatives and producer groups may soon own and manage their own blockchain-based agricultural networks, reducing reliance on big tech firms.

4. Regulatory Adoption
Governments may make blockchain mandatory for food exports or quality certifications, helping standardize traceability.
Final Thoughts
In a world that demands food safety, ethical sourcing, and sustainability, blockchain in agriculture is no longer a buzzword—it’s a necessity. By enabling food supply chain transparency using blockchain, farmers, consumers, and businesses can build a future based on trust, efficiency, and accountability.
From reducing food fraud to empowering smallholders in export markets, the impact of blockchain technology in farming is already being felt—and it's only the beginning.
Whether you’re a grower, buyer, policymaker, or tech innovator, one thing is clear: the path to a transparent, sustainable, and secure food system runs on blockchain.







