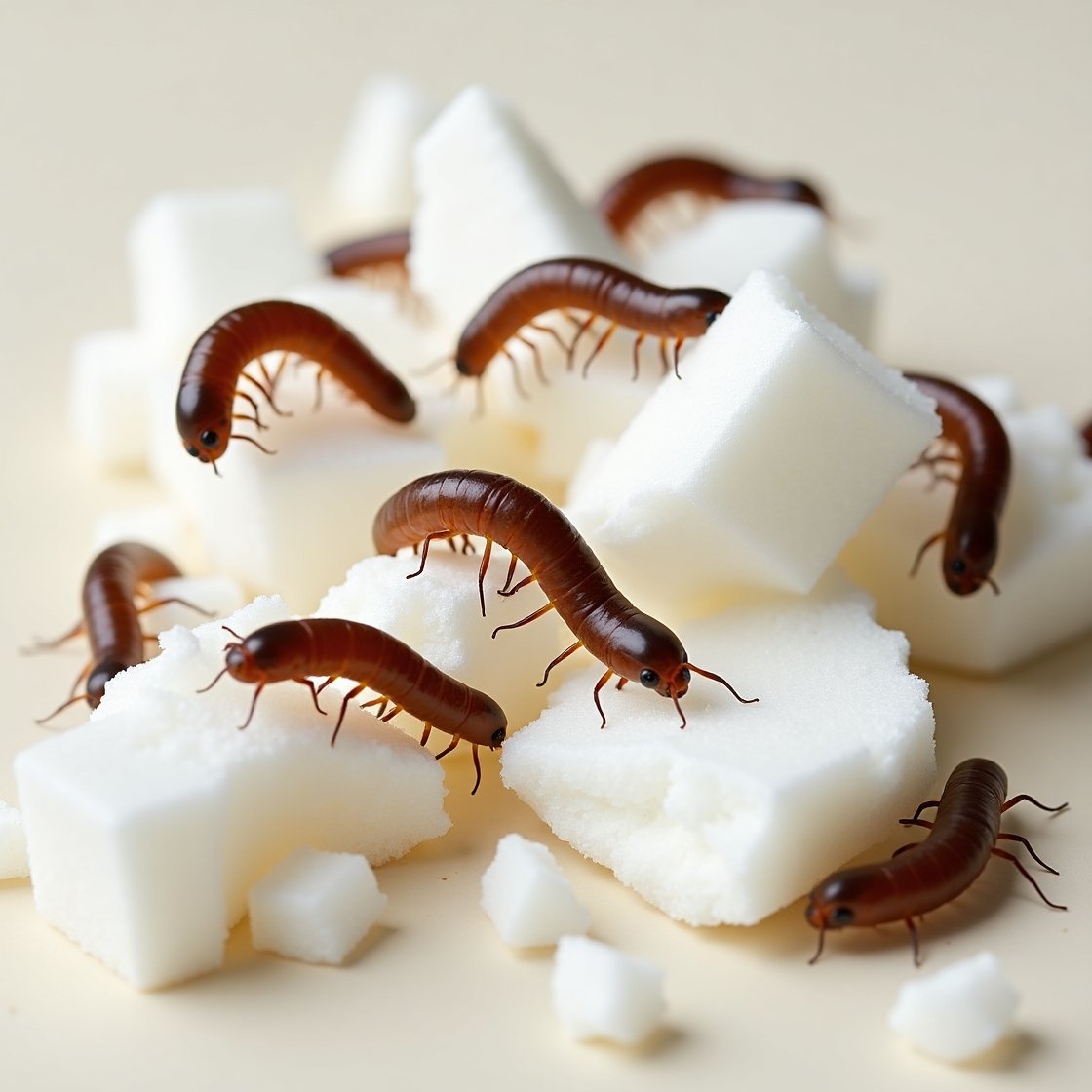
In recent years, researchers have uncovered a surprising discovery: mealworms eat plastic. These tiny larvae of the darkling beetle have been observed chewing through polystyrene, polyethylene, and even Styrofoam—materials once thought to be nearly indestructible. While this breakthrough has sparked hope for tackling global plastic pollution, it also raises important questions about the environmental and health risks involved.
Are these worms really the miracle solution we’ve been waiting for, or could their plastic-filled diets introduce new dangers into ecosystems and food chains? This blog explores how mealworms eat plastic, what science says about their digestive abilities, and whether this phenomenon is truly safe.
What Does It Mean That Mealworms Eat Plastic?
When researchers first observed that mealworms eat plastic, it shocked the scientific community. For decades, plastic waste has been one of the hardest pollutants to eliminate because it doesn’t biodegrade easily. Yet mealworms were seen munching on Styrofoam cups and packaging, reducing it to smaller particles and partially digesting it in their gut.
The process is made possible by specialized gut microbes that help break down long plastic polymers into smaller molecules. This ability suggests that mealworms could potentially play a role in reducing the mountains of plastic waste piling up in landfills and oceans.
But just because mealworms eat plastic doesn’t automatically mean it’s safe. That’s where concerns begin.

Why Scientists Study How Mealworms Eat Plastic
Researchers are fascinated by the fact that mealworms eat plastic because it opens up new avenues for waste management. Traditional recycling methods often fail because plastics are difficult and expensive to process. If mealworms can convert plastics into simpler compounds naturally, they could provide a cost-effective, biological alternative to recycling.
However, while studies confirm that mealworms can survive on a plastic diet, the efficiency is relatively low. A single mealworm can only consume a small amount of plastic daily. Scaling this up to tackle global waste requires millions—or even billions—of worms, which introduces new environmental challenges.
Health Risks When Mealworms Eat Plastic
The phrase mealworms eat plastic might sound promising, but the process raises several potential health risks:
1. Microplastic Formation
Mealworms don’t fully digest plastic; instead, they fragment it into tiny microplastics. These particles can leach into soil and water, spreading pollution in a more subtle form.
2. Toxic Chemical Transfer
Many plastics contain additives like flame retardants, plasticizers, and dyes. When mealworms eat plastic, these chemicals may accumulate in their bodies. If mealworms are used as animal feed or accidentally enter food chains, toxins could be passed along.
3. Unknown Gut Byproducts
The microbes that allow mealworms to eat plastic may also produce intermediate compounds. Some could be harmless, while others may pose risks we don’t fully understand yet.
4. Food Chain Contamination
In some regions, mealworms are promoted as protein-rich food for fish, poultry, and even humans. But if mealworms eat plastic before entering the food system, they could carry contaminants.
Environmental Concerns When Mealworms Eat Plastic
Beyond health risks, there are environmental questions to consider:
- Waste Mismanagement Encouragement: If society believes that mealworms eat plastic safely, industries may reduce efforts to cut plastic production. This could worsen overall pollution.
- Ecosystem Balance: Large-scale farming of mealworms for plastic waste disposal could disrupt ecosystems, particularly if non-native worms are introduced.
- Incomplete Solutions: Since mealworms eat plastic slowly and partially, they cannot replace systemic changes like reducing plastic production, improving recycling infrastructure, and adopting biodegradable alternatives.
Are There Benefits When Mealworms Eat Plastic?
It’s not all negative. Scientists are investigating how mealworms eat plastic to uncover potentially safe applications:
- Biodegradation Research: By studying the enzymes and gut microbes that let mealworms eat plastic, scientists may one day engineer more efficient microbial solutions.
- Plastic Waste Reduction: Small-scale tests show that Styrofoam waste can be reduced by letting mealworms eat plastic, preventing some of it from accumulating in landfills.
- Biotechnology Innovations: Understanding how mealworms eat plastic could inspire new industrial processes for tackling persistent pollutants.
Still, safety must remain the priority.
Should Mealworms Eating Plastic Be Encouraged?
The big question is whether we should actively encourage this process. While mealworms eat plastic, relying on them as the main solution is risky. The long-term effects of introducing plastic-fed worms into ecosystems or food chains remain unclear.
Instead, most experts recommend using mealworm research as a stepping stone toward safer, scalable technologies. For example, isolating the plastic-degrading microbes and enzymes from mealworm guts could lead to controlled laboratory applications without releasing worms into unpredictable environments.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Governments and environmental agencies are beginning to recognize the complexity of this issue. If mealworms eat plastic becomes part of waste management strategies, regulations will need to address:
- Safety testing for animal and human exposure.
- Guidelines for handling microplastics created during digestion.
- Ethical considerations of farming insects for waste disposal.
Without strict oversight, promoting mealworms as a quick fix could create more problems than it solves.
Conclusion: The Future of Mealworms Eating Plastic
The discovery that mealworms eat plastic is both fascinating and controversial. On one hand, it offers hope for reducing the overwhelming tide of plastic waste. On the other, it poses serious questions about health, safety, and sustainability.
For now, the safest path forward is continued research. Instead of seeing mealworms as the ultimate solution, we should treat them as an important clue in the search for better biodegradation methods. By combining scientific innovation, responsible regulation, and global efforts to reduce plastic production, we may one day transform the way we deal with plastic pollution.
Until then, the fact that mealworms eat plastic should inspire both curiosity and caution—because every solution comes with its risks.







